Are there any limits Termbase (TB) size?
For MultiTerm databases on the GroupShare server, the maximum number of entries is limited only by the available storage capacity.
How is access to TBs managed?
TTN TMS provides dynamic access rights that are automatically granted and revoked as needed. All users can access MultiTerm Online; however, clients typically have read-only permissions, while translators have read/write permissions. Access rights are verified and assigned automatically when an order is allocated to a translator or proofreader.
Is it possible to modify the TB structure for special use?
In most situations, a glossary containing only the source and target term is sufficient. However, in specialised domains such as medical translation it is often essential to extend the termbase with additional fields. For example, a simple bilingual glossary might contain only the entry “angioplasty – angioplastie” (English – French). By adding extra fields, the same entry can hold much richer information. A Definition field can describe the concept, for instance: “A surgical procedure to restore blood flow through an artery by inflating a tiny balloon.” A Reference or Source field can indicate the origin of this definition, such as “World Health Organization guidelines (2021).” A Context field can store a typical usage example: “The patient underwent angioplasty to open the blocked artery.”
With these fields in place, translators immediately see the precise meaning of the term. The definition explains the concept in clear language, which is crucial in cases where ambiguity is possible. The reference field points to an authoritative source or standard, increasing confidence in the information. This reduces the risk of errors and helps ensure that all translators use the term consistently.
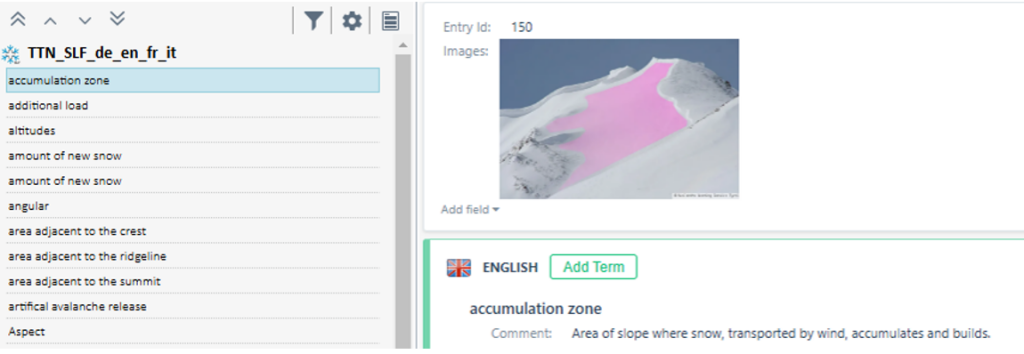
Figure 1: Termbases with comment and image
In other disciplines, such as meteorology, an image of a specific cloud type may be useful, while in nivology an image of an avalanche or a particular snow type can be invaluable. All these features are fully supported by MultiTerm. Fields such as Source, Notes, Definition, Reference, Context or Image can be added to the
How is search performed in termbases?
For terminology management, Trados GroupShare (via MultiTerm Server) likewise fulfils all search requirements. The system offers both exact‑term lookup and fuzzy‑term search in termbases, allowing entries to be found either by exact matches or by terms with slight spelling or wording variations. MultiTerm search can be configured to retrieve terms even when the query is not an exact match, using fuzzy matching to identify similar terms and returning them with a relevance score. This ensures that no relevant term is overlooked, even when the query contains minor differences or typos.
All defined fields of a term entry are displayed as part of the search results or when viewing an entry, including all compulsory fields such as term, translation, definition, context sentence and usage note.
How are termbase entries recognized and displayed?
In the translation environment, terms from connected termbases (TBs) are automatically recognized and clearly marked within the source segment. This ensures the translator can immediately access each term’s complete entry and view all required information at a glance. The system’s terminology component provides comprehensive support for terminology detection through features such as:
- Automatic Term Detection: Terms stored in the termbase are automatically identified when they appear in the source segment.
- Visual Term Highlighting: Each detected term is clearly marked (highlighted) within the source text for easy visibility to the translator
- Quick Term Entry Access: Users can quickly access the full termbase entry for any highlighted term directly from the interface (for example, by hovering over or selecting the term), immediately revealing all associated term details.
- Full Field Visibility: All mandatory and custom fields linked to each term (such as source references, definitions, and usage notes) are displayed as part of the term’s entry information, ensuring the user can view all relevant term data within the environment.
How are termbases managed?
The translation management system provides comprehensive features for managing termbases. It combines automated processes with administrator control to ensure effective and flexible resource management. Key aspects include:
The system automatically handles termbase setup based on project language pairs. When a project involves a previously unused source–target language combination, the system generates new TBs using predefined templates and parameters.
How do translation managers control termbases?
Administrators or translation managers have full control over all termbases. They can manually create, modify, or delete TBs and adjust their structure (for example, by adding or modifying fields and metadata) and content. The system also supports importing and exporting TB data for backup, migration, or integration purposes, giving the organization flexibility in managing linguistic assets.
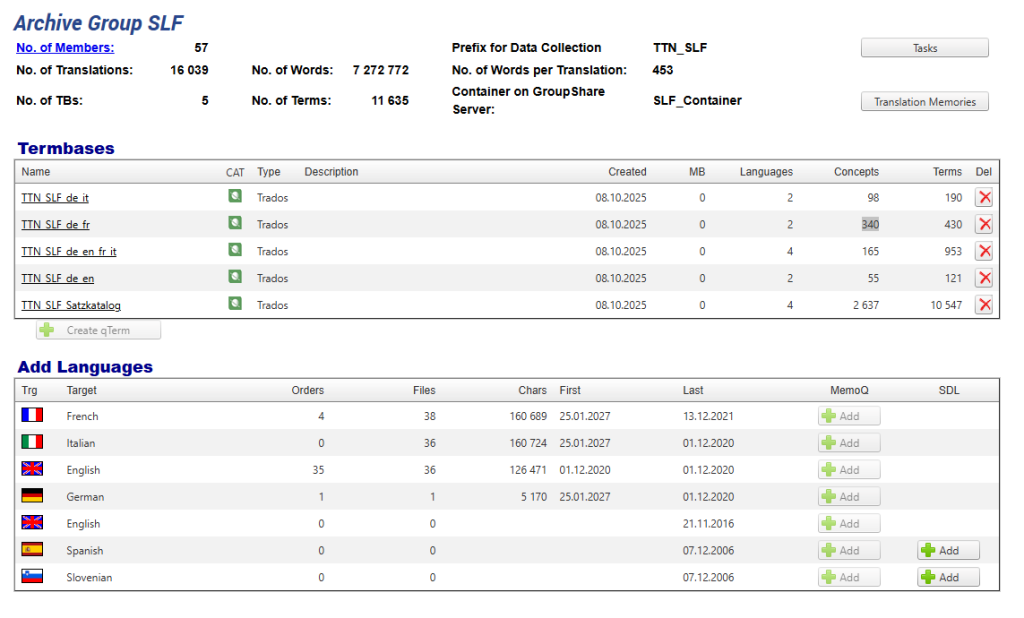
Figure 2: Create TBs with TTN TMS manually based on a predefined template
How are termbases customised?
By default, the system uses a standard termbase configuration for new language pairs, automatically creating a termbase only if none exists for the required source–target languages. If a specialized termbase is needed (such as one with custom fields or complex term structures), a translation manager can create or adjust it using an external terminology management tool (for example, a Trados MultiTerm application or a GroupShare terminology module). This manual method is more complex and typically used only when the default termbase configuration does not meet specific requirements.
By default, the system uses a standard termbase configuration for new language pairs, automatically creating a termbase only if none exists for the required source–target languages. If a specialized termbase is needed (such as one with custom fields or complex term structures), a translation manager can create or adjust it using an external terminology management tool (for example, a Trados MultiTerm application or a GroupShare terminology module). This manual method is more complex and typically used only when the default termbase configuration does not meet specific requirements.
In summary, the system automatically handles termbase management by creating or reusing resources as needed for new language combinations, while still allowing administrators to perform detailed oversight and customization when necessary. This ensures that enterprise clients benefit from both efficiency through automation and flexibility through administrator control in termbase management.