Are there any limits for TM size?
The number of segments in a translation memory is limited only by available storage space, which can be expanded dynamically.
How is access to TMs managed?
TTN TMS provides dynamic access rights that are automatically granted and revoked as needed. All users can access MultiTerm Online; however, clients typically have read-only permissions, while translators have read/write permissions. Access rights are verified and assigned automatically when an order is allocated to a translator or proofreader.
Is it possible to adapt TM fields for special use?
In legal or technical translations—such as construction standards—it is often useful to add custom fields, for example a reference number or a link to the relevant article or norm. In such cases, the structure of the translation memory must be extended with mandatory custom fields.
Trados GroupShare supports translation memories with rich metadata. Each TM entry contains the source segment, target segment, and any number of custom fields defined by the organisation. These custom fields are fully supported in the GroupShare interface and APIs: they can be created through field templates, viewed and edited in the TM editor, and used as filter or search parameters.
How is search performed in translation memories?
How are “exact match” and “fuzzy match” searches handled, and how is it ensured that search works accurately in all languages?
Trados GroupShare server‑based translation memory component fully supports both exact‑match and fuzzy‑match search modes for segment lookup. Exact‑match search retrieves only 100% identical source segments, while fuzzy‑match search returns similar segments together with a similarity score. The TM search engine uses robust fuzzy‑matching algorithms to calculate match percentages, indicating how closely a new segment corresponds to an existing translation unit. This ensures comprehensive and accurate search results, as even partial matches are identified and presented with their relevance score.
All compulsory fields and metadata associated with each translation unit are available in the TM search results. Each hit displays the source and target segment together with the required metadata fields, including custom fields marked as mandatory and standard system fields such as creation date or author. The same search mechanisms apply to all languages supported by the system, ensuring consistent behaviour across multilingual content.
How does TTN TMS detect previously translated segments?
TTN TMS automatically detects previously translated segments and suggests them for reuse whenever a matching source segment is opened. The system finds both exact and fuzzy matches in the TM, presents each suggestion with contextual details and highlights any differences for partial matches, allowing the translator to easily choose and insert the preferred translation, which is clearly marked as coming from the TM.
- Automatic match insertion: The proposed system automatically detects any previously translated segments in the TM (both exact 100% matches and fuzzy partial matches). When a translator opens a new source segment, the TM is searched and the best matching translation is immediately inserted into the target segment. This ensures that translators reuse existing translations whenever possible, with no manual lookup needed for each segment.
- Multiple match browsing: If more than one TM match is found for a given source segment, the interface displays all the matches (along with their match percentages) for the user’s reference. The translator can easily browse through these suggestions and choose which one to use. For example, the system lists matches in the Translation Results pane and allows the user to insert an alternate match instead of the top-ranked one. This gives the user full control to pick the preferred translation when multiple options exist.
- Match metadata visibility: For each TM result, the system provides additional context and metadata about the match. The translator can see information such as which TM the match came from, and other attributes like the original document or file name if available. This metadata is displayed alongside the match entry, helping users assess the origin and reliability of each suggestion.
- Highlighted differences for partial matches: When a stored translation is only a partial match to the new source segment, the system clearly highlights all differences between the source text and the TM suggestion. Any words or phrases that differ are indicated in the comparison (for example, with added text underlined in one colour and deleted text shown with strikethrough in another colour). This lets the translator immediately see what changes are needed, as differences are presented in a “track changes” style for easy identification.
- Clear marking of inserted TM content: Segments that have been pre-filled or inserted from TM matches are visibly marked in the editing environment. For instance, an icon or badge in the segment’s status column denotes that the content came from a TM match and even shows the match percentage. This way, translators and reviewers can instantly recognize which target segments were populated from the TM (and at what match level), ensuring transparency. Once the translator edits or confirms the segment, the indicator updates accordingly to show that the translation has been reviewed, while still retaining the original match information for reference.
All of these features are fully supported by TTN TMS’s translation memory component, ensuring that previous translations are leveraged efficiently while giving translators full control and visibility. This TM matching mechanism not only increases productivity by reusing existing translations but also provides translators with clear information and options to maintain translation quality and consistency.
How does TTN TMS integrate Machine Translation with TM?
TTN TMS seamlessly combines advanced Machine Translation (MT), Translation Memory (TM), and terminology management into a unified workflow. This integrated approach enables the use of both human-reviewed translations and AI-generated suggestions. The result is higher-quality output with reduced effort, delivered through intelligent automation that accelerates projects without compromising accuracy.
- Automatic MT suggestions when no TM match: When a new segment has no existing TM match, TTN TMS automatically provides a machine translation suggestion. This suggestion can be inserted directly into the target text or presented for review, ensuring that the translator does not start from a blank page. Even when the translation memory contains no entry, an initial draft translation is always available, reducing manual effort and saving time.
- MT suggestions alongside TM matches: TTN TMS does not rely on a single source of suggestions. When a fuzzy or exact TM match is available, the system can retrieve a parallel MT suggestion and display it alongside the TM result. This side-by-side presentation allows linguists to select the most appropriate option or combine elements from both suggestions. By presenting MT and TM results together, the platform increases translation quality and flexibility while continuing to benefit from existing translations and recent AI translation improvements.
- Integration with custom MT engines (Azure, DeepL, etc.): The solution is engine-agnostic and vendor-neutral. TTN TMS integrates with leading MT providers such as Microsoft Azure Translator, DeepL, and other AI services, including GPT-based engines such as ChatGPT. Custom-trained models can also be connected via API. This flexibility enables the use of preferred machine translation engines to generate higher-quality suggestions. As new MT technologies emerge, they can be integrated seamlessly, ensuring long-term adaptability and continued access to state-of-the-art AI translation capabilities.
- Conversational AI for Context and Terminology: TTN’s conversational AI layer adds an additional dimension to translation productivity. Traditional translation memory systems and terminology databases often struggle to operate optimally together; for example, a fuzzy TM match may not automatically incorporate approved terminology. The GPT-based conversational AI layer addresses this limitation by intelligently combining TM matches with approved terminology in context, generating refined translation suggestions that respect both sentence context and terminology constraints.
By leveraging advanced GPT-based AI within TTN TMS, the system analyses each segment together with relevant TM fragments and required glossary terms to produce fluent translations that seamlessly integrate these elements. The resulting output is not a generic machine translation, but a suggestion informed by existing translations and established terminology, assembled through an AI-driven process that accounts for nuance and context. This approach frequently outperforms traditional MT engines in terms of accuracy and consistency.
The conversational AI layer significantly reduces the need for repeated terminology corrections or manual reworking of fuzzy matches. Translators receive high-quality draft translations that already comply with glossaries and style guidelines, thereby reducing post-editing effort. Overall, TTN TMS’s MT–TM integration, enhanced by an intelligent AI layer, delivers consistent, terminology-compliant translations from the outset while accelerating delivery timelines.
How are TMs managed?
The translation management system provides comprehensive features for managing translation memories and termbases. It combines automated processes with administrator control to ensure effective and flexible resource management. Key aspects include:
The system automatically handles translation memory and termbase setup based on project language pairs. When a project involves a previously unused source–target language combination, the system generates a new TM and TB using predefined templates and parameters, ensuring a dedicated resource for that language pair. If an appropriate TM or TB already exists covering the required language pair, the system reuses the existing resource instead of creating a duplicate.
How do translation managers control TMs?
Administrators or translation managers have full control over all translation memories. They can manually create, modify, or delete TMs and adjust their structure (for example, by adding or modifying fields and metadata) and content. The system also supports importing and exporting TM data for backup, migration, or integration purposes, giving the organization flexibility in managing linguistic assets.
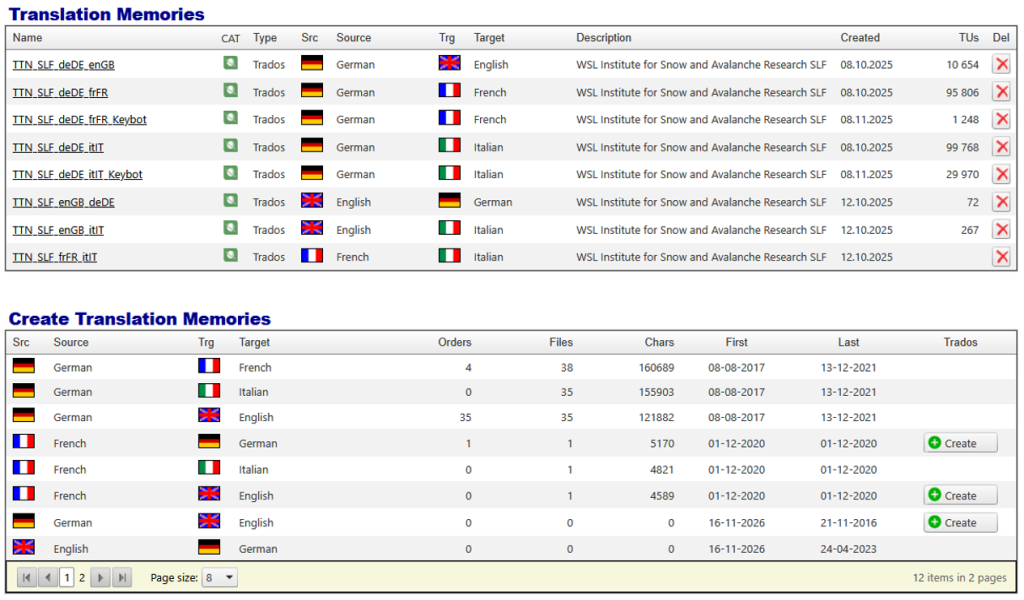
Figure 1: Create TM with TTN TMS manually based on a predefined template
Structural Adjustments via GroupShare: If a translation memory requires advanced structural changes beyond the default template (for example, adding custom fields), a translation manager or system operator can connect directly to the underlying TM server (for example, an SDL Trados GroupShare server) to apply these modifications. This approach ensures that specialized configurations can be implemented even if it requires using tools beyond the default web interface.
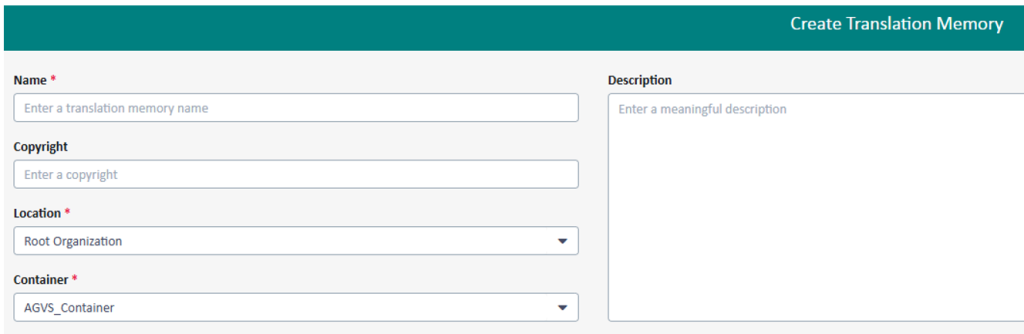
Figure 2: Create translation memory with special field directly on the GroupShare server
In summary, the system automatically handles translation memory and termbase management by creating or reusing resources as needed for new language combinations, while still allowing administrators to perform detailed oversight and customization when necessary. This ensures that enterprise clients benefit from both efficiency through automation and flexibility through administrator control in TM and TB management.
In a TTN TMS environment with SDL Trados GroupShare integration, translation segments saved by one user in a shared translation memory (TM) immediately available to other authorized users. GroupShare is a server-based collaboration solution that centralizes TMs, so when one team member confirms a segment, it instantly updates for all other users who have the appropriate access privileges. This means the latest translations are accessible across the team without delay, enabling true real-time collaboration.
GroupShare achieves this through its centralized TM and terminology database. As soon as a translator saves a new translation unit, it’s stored on the server and can be retrieved by others right away. For example, if one translator confirms a new translation for a segment, any colleague who later encounters that same source text will immediately see the translation as a 100% match from the TM. Similarly, if a user adds a term to the shared termbase, others will see it appear instantly as a recognized term in their translation tool. This immediate synchronization ensures all team members are always working with the most current translations and agreed terminology.
By providing real-time updates to the shared TMs and termbases, GroupShare helps maintain consistency and facilitate teamwork. All users are effectively working with the same up-to-date set of approved translations and terms in one secure, unified environment. This not only improves the overall consistency and quality of the translations, but also makes collaboration between translators and reviewers much more efficient, since everyone is leveraging the latest confirmed segments and terminology.